Photo by Ryan Everton on Unsplash
Have you ever opened up the dishwasher machine after a cycle only to see that residual water is on the plastics inside? What was your thought at that exact moment? "Is the dishwasher working properly?" Do not panic; the dishwasher is working. Plastic containers absorb heat at different rates than metals.
Specific Heat Capacity
I will just cut to the chase. The specific heat capacity is responsible for different materials drying in dishwashers in a given time. Plastic has a much different specific heat capacity than does water. What does the difference mean? The rate of thermal energy absorbed by a material depends on the specific heat capacity:
The specific heat capacity is the amount of heat required to raise a gram of material a single degree on the Celsius temperature scale.
The table below shows that materials absorb heat at different rates:
The lower the specific heat capacity of the substance, the less heat is required to change the temperature a single degree Celsius.
In the table above, the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a gram of water (4.186 Joules/gram C) is roughly eight times the amount to change a gram of steel (0.490 Joules/gram C).
How About Plastic?
The plastic container below is a standard container found in a domestic dishwasher.
Plastic, in general, is made up of a high molecular weight polymer. A polymer is a large molecule of repeating units (i.e., molecular units). In the case of Rubbermaid, the small repeating molecular units are shown below:
The molecule above is a repeating unit of polycarbonate. Meaning that the molecule above is a link in a chain. On one side of the molecule is the polycarbonate portion of the chain. The polycarbonate part of the repeating molecular unit is shown below circled:
The dashed ends of the repeating unit with a bracket indicate that the molecule is a link of a more massive chain (of repeating units). Polymers differ in the number of repeating units. The molecular weight of a polymer is dependent on the number of repeating units. The best example of a high molecular weight polymer is a car tire. As a side note, a car tire is an example of a massive polymer - a single polymer chain - a huge chain.
According to the table above with various specific heat capacities, the specific heat of plastic is between the value for steel and water. Water holds heat very well. Whereas, the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a gram of plastic is double the amount needed to raise a gram of steel.
Heat Transfer Inside A Dishwasher
Hot water circulating in dishwasher heats objects (metals, plastics, etc.). Pots and pans absorb heat from the warm flowing water. The water reaches a maximum of 75 Celsius during the cleaning cycle. Hot water circulating removes food from metal containers and plastics.
There is the last rinse cycle, which increases the temperature of the water an additional 7 Celcius to reach a maximum temperature of 82 Celcius (180 F). The last rinse step dries the dishes.
Specific heat accounts for the heat absorbed to raise the temperature. Heating objects depends on absorbing thermal energy inside a dishwasher:
The thermal energy absorbed by heating (energy = Joules) is dependent upon: mass (in grams), specific heat capacity (Joules/gram C), and the Temperature range (Final-Initial).
Heating inside of a dishwasher depends on the three parameters shown above.
Therefore, the reason why plastic does not dry inside of the dishwasher is due to the large specific heat capacity. Certain plastics might dry which are not made of polycarbonate and possess a lower specific heat capacity.
Metal objects have low specific heat capacities. Which means that during a dishwasher cycle, the metal objects will experience a broad temperature range - heat up quickly to a high temperature. Whereas plastics have sizeable specific heat capacities.
Therefore, the temperature range which plastics undergo throughout a dishwasher cycle will be lower, which means that the water will not evaporate off of a piece of plastic which does not heat up to the equivalent temperature of steel or aluminum.
Dishwashers were not initially designed to heat plastics. Early models were calibrated to heat metal objects. Plastic containers placed on the bottom shelf could experience inhomogeneous (i.e., non-uniform) heating, which would result in changing shape. Yes, the plastic would dry, but be deformed.
To attempt to dry plastic containers, place them on the top shelf. Be sure to clean the plastic in the sink (of all food) first before placing the objects in the dishwasher. That way, all the heat absorbed during the rinse cycle can be converted into heat to evaporate water (i.e., dry). That is the best strategy.
Related Blog Posts:
1) Dimensional Analysis Of Statistics And Large Numbers - Index Of Blog Posts
2) Science Topics, Thoughts, and Parameters Regarding Science, Politics, And The Environment!
Related Blog Posts:
1) Dimensional Analysis Of Statistics And Large Numbers - Index Of Blog Posts
2) Science Topics, Thoughts, and Parameters Regarding Science, Politics, And The Environment!

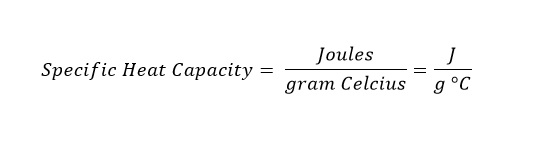





No comments:
Post a Comment